Different countries and cultures worldwide have used medicinal plants for thousands of years. Several studies have looked into the usefulness of these medicinal plants. However, more research is still ongoing to understand the medical benefits better. This article provides basic information about specific medicinal plants and what the science says now. For more information, visit Herbs At a Glance.
1. Ginseng
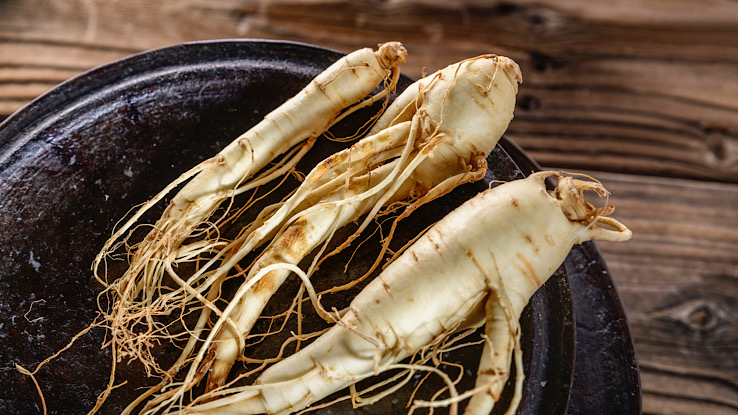

American ginseng is one of the most widely used plants in herbal medicine. People crush the root and take it orally. People take it to boost their immune systems, decrease stress, and help treat upper respiratory infections. Ginseng is in soft drinks and cosmetics and is in high demand worldwide. People sometimes confuse American ginseng and Asian ginseng, but they have different properties.
2. Echinacea
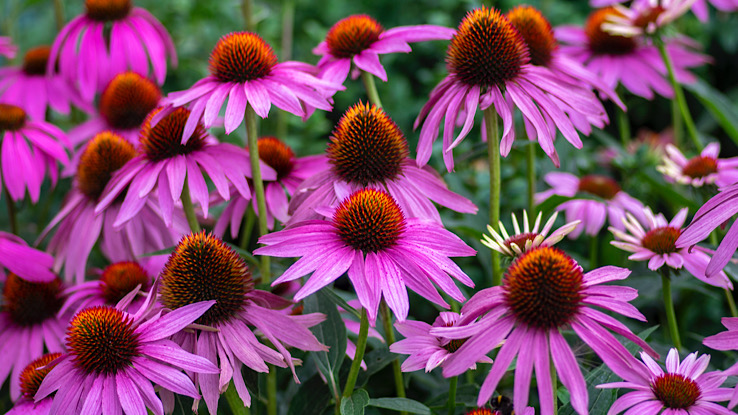

Echinacea, also known as coneflower, can prevent and treat colds and help fight infection. People also use it for wounds on the skin and to treat skin conditions.
3. St. John’s Wort

People use St. John’s Wort either on your skin or take it by mouth. Common topical uses include healing wounds or bruises and lessening muscle pain. Taking the plant by mouth may help with depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). However, St. John’s Wort can interact badly with some medications, so talk to your doctor before taking it.
4. Milk Thistle

You can find ,ilk thistle, also known as silymarin, on most continents. You can take this supplement orally. Milk thistle can be helpful to those with diabetes, hepatitis C, indigestion, and cirrhosis.
5. Sage

Many cultures use Sage for health benefits and as a spice. People use sage for sore throats, memory loss, diabetes, and to manage cholesterol levels. However, sage has high levels of thujone, and you should not eat it in large amounts since it may cause seizures.
6. Ginkgo

In the past, people used leaf extracts from the ginkgo tree for asthma, bronchitis, and kidney issues. People have recently used ginkgo extract as a dietary supplement for memory loss, tinnitus, and anxiety. People only use the leaf extracts, because the seeds contain toxins.
7. Chamomile
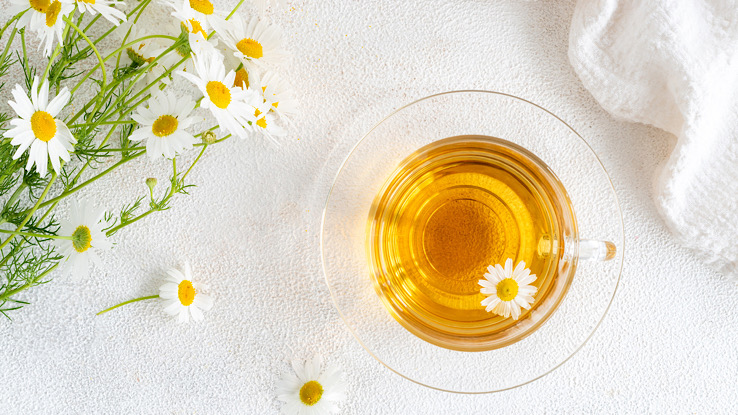

There are two different types of chamomile, Roman and German.
- German chamomile: People use it for indigestion, insomnia, and high stress. It can also treat sores on the gums caused by cancer treatment.
- Roman chamomile: People use it for insomnia, nausea, and swelling. You can put it in teas and on the skin for wounds and inflammation.
8. Aloe Vera
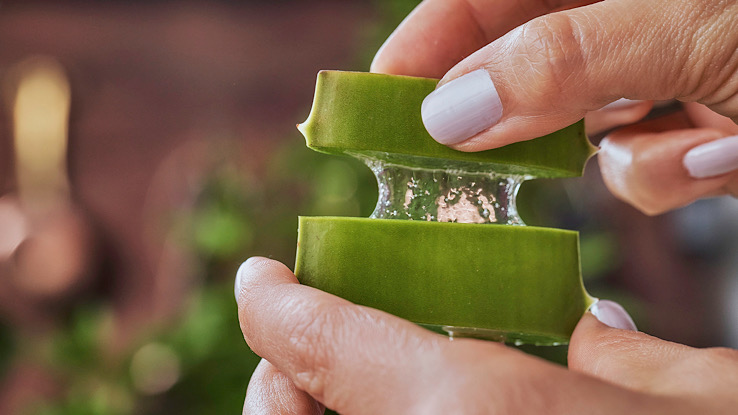

There are over 400 kinds of aloe plants. Aloe vera has a gel within the leaves that can treat burns on the skin. People also use the leaves as a laxative. You will find this plant in commercial foods and as a flavor additive and dietary supplement.
9. Tea Tree
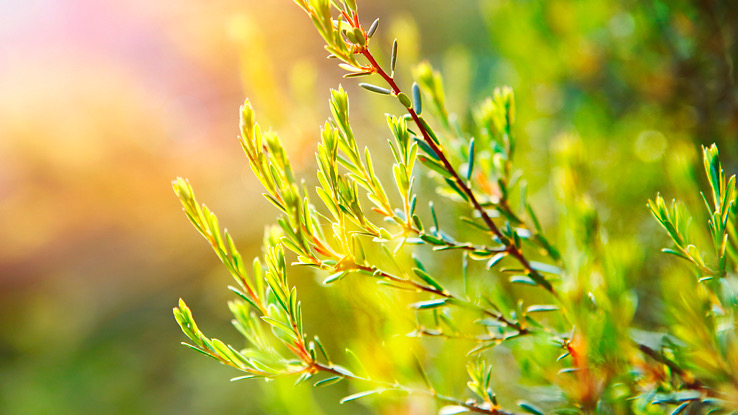

The oil made from tea tree leaves can be very beneficial for the skin and help treat acne. It is also an antiseptic and can be helpful for insect bites, nail fungus, and cuts. You should use tea tree oil topically and not eat it.
10. Valerian
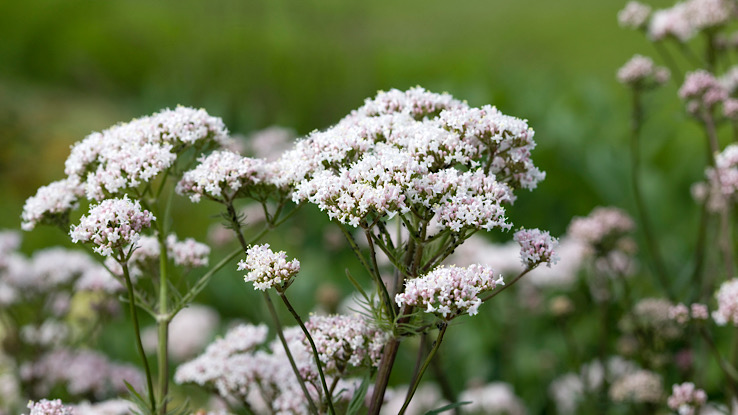

The roots of this plant can treat insomnia, anxiety, and migraines. Studies show that valerian can help relieve premenstrual syndrome (PMS) pain and menopause symptoms. Since it can help induce sleep, do not use it with alcohol or sedatives.
Resource Links
- “Aloe Vera” via National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- “Aloe” via Mayo Clinic
- “American Ginseng” via MedlinePlus
- “Chamomile” via National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health
- ‘Echinacea: What Should I Know About It?” via Family Doctor
- “The growing use of herbal medicines: issues relating to adverse reactions and challenges in monitoring safety” via Frontiers in Pharmacology
- “A Guide to Common Medicinal Herbs” via University of Rochester Medical Center