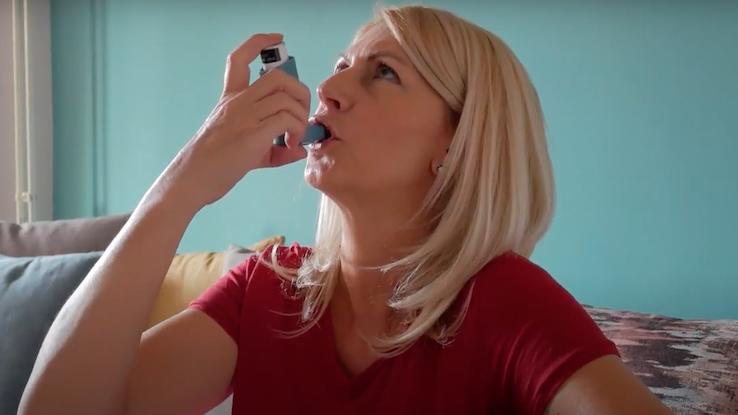
Like most organs, your lungs play a vital role in your overall health and your body’s ability to function properly. And, like most organs, your lungs can also develop a variety of conditions that impact your health. Understanding the symptoms that are common markers of lung disease can empower you to take charge of your health, recognize warning signs and seek treatment early on when there’s an improved chance of recovery.
What Is Pulmonary Lung Disease?
The term “pulmonary lung disease” is somewhat of a misnomer. The word “pulmonary” itself describes anything related to your lungs, “pulmonary lung disease” refers to lung disease. And lung disease refers to several different conditions that can damage or otherwise cause health issues with your lungs. Many of these disorders make it difficult to breathe or prevent your body from getting enough oxygen.
There are three primary types of lung disease. Airway diseases cause narrowing or blockages in your airways, which are the tube-like structures that carry air into your lungs. They may make you feel as though you’re unable to draw enough oxygen into your lungs. Lung tissue diseases develop due to scarring or other structural issues within your lung cells They can make you feel like your chest can’t expand enough to take full, deep breaths or fully expel all the air in your lungs. Circulation diseases affect the blood vessels in your lungs and also make it difficult for your lungs to take in and release oxygen. These circulatory conditions can also affect your heart while making your breathing labored or causing shortness of breath. Some of the most common lung diseases include asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) and lung cancer.
Currently, researchers don’t know about every cause of lung disease, but they do know that some lifestyle factors and exposure to certain contaminants can lead people to develop lung disease. Smoking tobacco products is one of the most well-known causes of lung disease — particularly lung cancer. Even if you don’t smoke, breathing in secondhand smoke can raise your risk of lung disease. Quitting smoking can reduce your risk of developing lung cancer and other conditions. Long-term exposure to radon (a naturally occurring radioactive gas), asbestos (a group of natural minerals that were once widely used in consumer products) and air pollution can also cause lung disease.
Asthma Symptoms
Asthma causes your airways to narrow, making it difficult to breathe. This condition also makes your airways swell, resulting in wheezing, coughing and shortness of breath. It varies in severity from mild to life-threatening and often comes on as an “asthma attack,” meaning symptoms only appear when they’re triggered by exercise, allergens or other irritants like dust. However, symptoms can be present all the time in more severe cases.
In addition to shortness of breath, coughing and wheezing, other symptoms of asthma include pain and tightness in your chest and trouble sleeping due to an inability to breathe. When you get a cold or another type of respiratory illness, it may last longer than 10 days if you have asthma. The muscles in your chest may feel constricted, which contributes to the difficulty you have getting air into your lungs. This disease is often hereditary, meaning you’re more likely to develop it if someone in your immediate family also has it.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Symptoms
Like asthma, COPD is also an inflammatory condition that obstructs your airway. Having chronic bronchitis and emphysema concurrently is one of the most common causes of this condition. Chronic bronchitis develops when the linings of your bronchial tubes, which deliver air from your windpipe into your lungs, become inflamed. It causes a severe cough that produces mucus. Emphysema develops when the air sacs, which transfer oxygen and carbon dioxide to and from your bloodstream, in your lungs weaken and rupture. The primary symptom of emphysema is shortness of breath.
Most people who develop COPD had both emphysema and chronic bronchitis beforehand, so many of the symptoms overlap. They include a chronic cough that produces mucus, wheezing and shortness of breath while you’re doing basic activities like walking. As COPD worsens, it can cause severe chest pain and tightness and make you more susceptible to respiratory illnesses and infections. You may begin losing weight or feeling fatigued all the time. Advanced COPD can cause unintended weight loss because you may have difficulty breathing while you eat and because your damaged lungs burn many more calories trying to function.
Lung Cancer Symptoms
Lung cancer is a condition that develops when abnormal cells start growing uncontrollably in your lungs. These cells don’t grow into healthy lung tissue and don’t work the same way normal lung cells do. Instead, as they grow, they begin interfering with your lungs’ ability to function the way they should.
Symptoms of lung cancer often mimic those of other, less-serious lung issues, which is why it’s important to let your doctor know about any changes you notice in the way your chest feels or your ability to breathe. Early signs and symptoms of lung cancer include a persistent cough or a cough that produces blood, shortness of breath and general weakness. You may also experience pain in your chest, back or shoulders that gets worse when you try to take a deep breath, laugh or cough. You might start to wheeze when you breathe, and your voice may become hoarse.
Because it can take years for lung cancer to develop to the point that you experience symptoms, it’s important to make an appointment with your doctor immediately if you notice these symptoms aren’t going away.
Resource Links:
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000066.htm
https://medlineplus.gov/lungdiseases.html
https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/lung-disease
https://www.lungcancer.org/find_information/publications/163-lung_cancer_101/265-what_is_lung_cancer
https://www.cancercenter.com/cancer-types/lung-cancer/symptoms
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/asthma/symptoms-causes/syc-20369653
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/emphysema/symptoms-causes/syc-20355555
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/copd/symptoms-causes/syc-20353679